SPSS LTRIM Function
Summary
SPSS LTRIM (left trim) removes leading spaces from string values. These occur especially when converting numbers to strings by using the stringfunction.The reason this occurs is that SPSS' default alignment for numeric variables is right and string values are always padded with spaces up to the length of their containing variable. For removing trailing rather than leading spaces, see RTRIM.
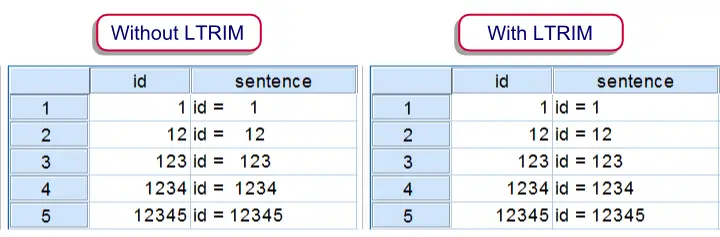 Results of CONCAT with and without LTRIM
Results of CONCAT with and without LTRIM
SPSS Ltrim Example
The syntax below demonstrates a situation where you'll like to use LTRIM. Running step 1 simply creates a mini dataset. Step 3 uses CONCAT without LTRIM and thus results in a values containing undesired spaces. Finally, step 4 shows how to avoid these by using LTRIM. The results of steps 3 and 4 are shown in the above screenshot.
SPSS Ltrim Syntax Example
data list free / id(f5).
begin data
1 12 123 1234 12345
end data.
*2. Declare new string variable.
string sentence(a10).
*3. Results in undesired spaces before numbers.
compute sentence = concat("id = ",string(id,f5)).
exe.
*4. Ltrim undesired spaces and then concatenate.
compute sentence = concat("id = ",ltrim(string(id,f5))).
exe.
SPSS REPLACE Function
Definition
SPSS REPLACE replaces a substring in a string by a different (possibly empty) substring.
SPSS Replace - Removing Spaces
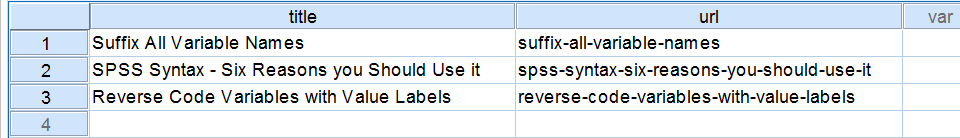 URLs are created from "title" by using REPLACE. The syntax below demonstrates how to do this.
URLs are created from "title" by using REPLACE. The syntax below demonstrates how to do this.
We have a dataset holding the titles of web pages and we'd like to convert these to URLs. For one thing, we don't like spaces in URLs. The syntax below shows how to remove them. Step 1 creates a tiny dataset (just run and otherwise ignore it) and step 3 demonstrates how to remove spaces using REPLACE.
SPSS Replace Syntax Example 1
data list free/title(a50).
begin data
"Suffix All Variable Names"
"SPSS Syntax - Six Reasons you Should Use it"
"Reverse Code Variables with Value Labels"
end data.
*2. Declare new string variable for URL.
string url(a50).
*3. URL is title with spaces removed.
compute url = replace(title,' ','').
exe.
SPSS Replace - Replacing Spaces
- Removing all spaces from our titles doesn't make our URLs very readable. We'll therefore replace all spaces in
titleby dashes. Note that this may require RTRIM so we added that in step 4 below.Precisely,RTRIMis applied automatically in Unicode mode so in that case it may be omitted. However, we recommend using it anyway to stay on the safe side. - Note that this creates a new problem: URLs for titles that contain "
-" now have triple dashes. However, we can simply useREPLACEagain for correcting these. - In practice, we usually like our URLs in lowercase only. After doing so in step 6, our URLs are as desired.
- Using consecutive string modifications for arriving at the desired result as done here is perfectly fine. Job done. However, do realize that functions can be used within functions (referred to as substitution). This makes it possible to run all we've done so far in a single line. Steps 7 and 8 first erase
URLand then reconstruct it in one go.
SPSS Replace Syntax Example 2
compute url = replace(rtrim(title),' ','-').
exe.
*5. Replace triple dashes by single dashes.
compute url = replace(url,'---','-').
exe.
*6. Convert URL to lowercase.
compute url = lower(url).
exe.
*7. Delete values from URL.
compute url = ''.
exe.
*8. Compute URL in one go.
compute url = lower(replace(replace(rtrim(title),' ','-'),'---','-')).
exe.
SPSS RTRIM Function
Summary
By default, SPSS right pads string values with spaces up to the length of their containing string variables. You don't usually see this but it may complicate concatenating strings. Such complications are avoided by trimming off trailing spaces using RTRIM (right trim). In Unicode mode, RTRIM is applied automatically but it's fine to use it anyway.
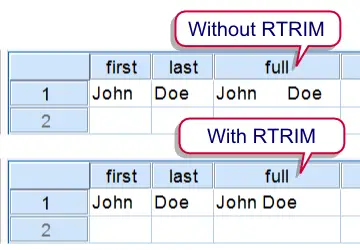 Results of steps 6 and 7 of the example syntax
Results of steps 6 and 7 of the example syntax
SPSS Rtrim Example
The syntax below demonstrates two complications that may result from omitting RTRIM. We recommend you run it and inspect the results after each step. Make sure you have no datasets open because they'll prevent SPSS from switching Unicode Mode off.
SPSS Rtrim Syntax Example
preserve.
set unicode off.
*2. Create mini dataset.
data list free / first last (2a10).
begin data
John Doe
end data.
*3. Declare new string variable.
string full(a10).
*4. Attempt 1. Concat does not seem to work.
compute full = concat(first,last).
exe.
*5. Increase string length.
alter type full(a20).
*6. Attempt 2. Results in excessive spaces.
compute full = concat(first,last).
exe.
*7. Attempt 3. Rtrim removes excessive spaces.
compute full = concat(rtrim(first),' ',rtrim(last)).
exe.
*9. Close all open data.
dataset close all.
new file.
*10. Restore system settings.
restore.
SPSS Rtrim Syntax Notes
- Wrapping all syntax between
PRESERVE.andRESTORE.ensures your system settings (in this case just Unicode Mode) don't change by running the syntax. - In step 4,
CONCATdoesn't seem to work. However, the real problem is that the concatenation results in a string value of 20 characters for a 10 character string variable. In this case, SPSS discards the last 10 characters that don't fit into this string. - The entire 20 character result can be seen by increasing the length of
fullto 20 characters by using ALTER TYPE in step 5. - Before you can switch Unicode Mode on or off, make sure there's no open datasets. This is done in step 9.
- Use LTRIM in case you need to remove leading rather than trailing spaces.
SPSS INDEX Function
The SPSS INDEX function returns the position of the first occurrence of a given expression within a string. If the expression does not occur in the string, it returns a zero. As a rule of thumb, always use it as CHAR.INDEX. The reason for this is explained SPSS Unicode Mode. Note that string values are case sensitive.
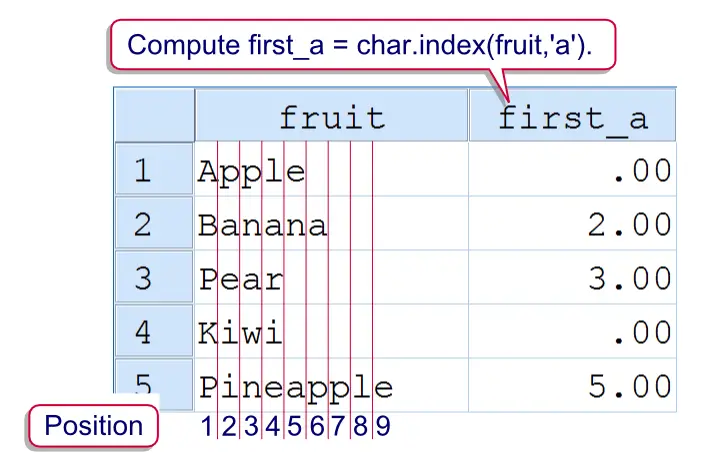 SPSS Index Function Example
SPSS Index Function Example
SPSS Index Example
Say we have data holding some email addresses and we'd like to see which domains are used most. For each email address, the domain is everything after the @ sign. The syntax below demonstrates how to do so. We'll first find the position of the first (and only)@ in step 2. Next, we'll substitute that into a SUBSTR function in step 4.
SPSS Index Syntax Example 1
data list free/email (a20).
begin data
[email protected] [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] maarten1979bkb.nl
end data.
*2. Find position of first "@".
compute first_a = char.index(email,'@').
exe.
*3. Declare new string variable for domain.
string domain(a15).
*4. Extract domain from email address.
compute domain = char.substr(email,char.index(email,'@') + 1).
exe.
*5. Correction for email without "@".
if char.index(email,'@') = 0 domain = ''.
exe.
Note that there's an error in the data since the last email address doesn't contain any @. Therefore, first_@ is zero for this case. This makes step 4 come up with an incorrect domain, hence the correction at the end.A better option here is to use a single IF command that computes the domain only if @ is present in the email address.
SPSS Index - the Divisor
A little known feature of SPSS' INDEX function is an optional third argument known as the divisor. The divisor divides the search expression into substrings of length n. The position of the first occurrence of one of these substrings is returned. For example, in CHAR.INDEX(variable,'0123456789',1) the divisor is 1. This breaks 0123456789 into substrings of length 1, rendering the digits 0 through 9. The position of the first digit is now returned.
The next syntax example extracts all digits from a string. It combines the use of the divisor with LOOP, SUBSTR and CONCAT in order to do so. The last step uses ALTER TYPE for converting it into a numeric variable.
SPSS Index Syntax Example 2
compute number_present = char.index(email,'0123456789',1) > 0.
exe.
*2. Declare new string.
string numbers(a20).
*3. Loop through characters and pass each digit into string.
loop #pos =1 to char.length(email).
if char.index(char.substr(email,#pos,1),'0123456789',1) > 0 numbers = concat(numbers,char.substr(email,#pos,1)).
end loop.
exe.
*4. Convert string to numeric variable.
alter type numbers(f1.0).
 SPSS TUTORIALS
SPSS TUTORIALS