- Python is Fully Case Sensitive
- Check Object Types in Python
- Indentation Matters in Python
- Python Assignment or Comparison Operator
- Escape Sequences in SPSS and Python
- Comments in SPSS and Python
Python is Fully Case Sensitive
Experienced SPSS users probably know that SPSS syntax is mostly case insensitive: it doesn't usually matter whether you write syntax in lower case, upper case or a mixture of these. Like so, the FREQUENCIES commands below are all equivalent.
FREQUENCIES V01 TO V10.
frequencies v01 to v10.
fReQuEnCiEs v01 tO V10.
In contrast, Python is fully case sensitive. As a consequence, you always need to use the exact right casing in Python or you may otherwise trigger a wide variety of errors and warnings.
begin program python3.
myName = 'Ruben'
print(myName) # Ruben
print(myname) # [...] NameError: name 'myname' is not defined
end program.
Note that you also need use the correct casing for SPSS variable names in Python. Avoiding all upper case for SPSS variable names tends to simplify things.
Check Object Types in Python
In SPSS, “data types” mostly refer to variable types. Keep in mind that “variables” in SPSS are columns of cells that hold data values. There's only 2 SPSS variable types:
- numeric variables and
- SPSS string variables.
These 2 types determine what you can (not) do with a variable in SPSS. Confusingly, the Type column in variable view suggests that there's many more variable types but these are formats, not types as explained in SPSS Variable Types and Formats.
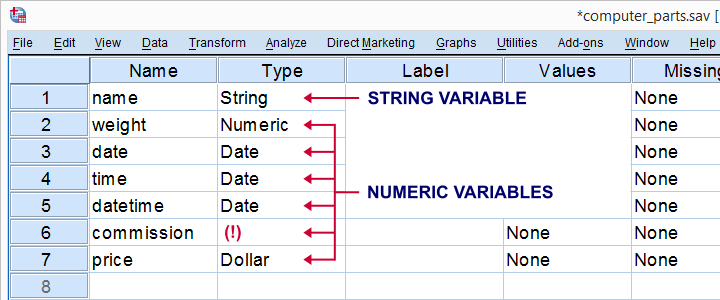
In Python, we'll also encounter strings and numbers but these are called objects instead of variables and only hold a single value. An entire column of values is usually represented as a Python list object or a Python tuple. And these are different object types than the strings or integers they may contain.
Like so, there's many different Python object types which we briefly cover in Quick Overview Python Object Types. Just as with SPSS variable types, Python object types determine what you can (not) do with them and how. That's why you sometimes need to check what type of object you're dealing with. This is simply done with print(type(myObject)) as shown below.
begin program python3.
myName = 'Ruben'
print(type(myName)) # <class 'str'>
end program.
Note: Python users can create new object types known as Classes. Such classes typically have their own methods and properties. You may need a bit of study for dealing with some of them.
Indentation Matters in Python
Basic looping in SPSS is done with
- a DO REPEAT or LOOP command indicating the start of some loop;
- 1(+) SPSS transformation commands that we'll loop over and
- an END REPEAT or END LOOP command in order to end some loop.
The syntax below briefly illustrates this structure.
do repeat #vars = v01 to v05.
compute #vars = 0.
end repeat.
In Python, the start of a loop is indicated by a for or while statement. After that, the indentation of the lines that follow indicate where a loop ends. The examples below illustrate how this works.
begin program python3.
for ind in range(10):
print('COMPUTE V{} = {}.'.format(ind,ind))
print("VARIABLE LABELS V{} 'Mean Job Satisfaction Score'.".format(ind))
end program.
*LOOP OVER 1 PRINT STATEMENT.
begin program python3.
for ind in range(10):
print('COMPUTE V{} = {}.'.format(ind,ind))
print("VARIABLE LABELS V{} 'Mean Job Satisfaction Score'.".format(ind))
end program.
This means that in order for your Python code to function properly, you must apply the correct indentation levels. This goes for
- Python
forloops; - Python
whileloops; - Python
ifstructures, possibly includingelifand/orelse; - Python try-except structures.
Note that we cover most of these in Conditions and Loops in Python.
Python Assignment or Comparison Operator
In SPSS syntax, the = operator is used for
- assigning a value or function to some variable as in COMPUTE or IF or
- comparing a variable/value to another variable/value.
The syntax below shows 2 minimal examples.
compute m01 = mean(v01 to v05).
*USE = FOR COMPARISON IN SPSS.
do if (gender = 0).
...
end if.
In contrast, Python uses
- = for assigning a value to some object but
- == for comparing and object/value to another object/value.
The examples below briefly illustrate the difference.
begin program python3.
myAction = 'PRINT' # = assigns value to object
if myAction == 'PRINT': # == compares values
print('FREQUENCIES ALL.')
end program.
For an overview of these and many other Python operators, read up on Python Operators - Quick Overview & Examples.
Escape Sequences in SPSS and Python
In SPSS, we rarely use escape sequences but 2 main exceptions are
- escaping a single quote in a value/variable label by doubling it and
- using \n in variable and value labels to have them break over 2 or more lines.
Few SPSS users are aware of such escape sequences but running the syntax below nicely illustrates both.
data list free/v01.
begin data.
6
end data.
*ESCAPE SINGLE QUOTE BY DOUBLING IT.
add value labels v01 6 'Don''t know'.
*ESCAPE "n" BY BACKSLASH.
variable labels v01 'This label continues on\nline 2 and\nline 3'.
*SHOW LABELS IN SUCCEEDING OUTPUT TABLES.
set tnumbers both tvars both.
*QUICK CHECK.
frequencies v01.
Result
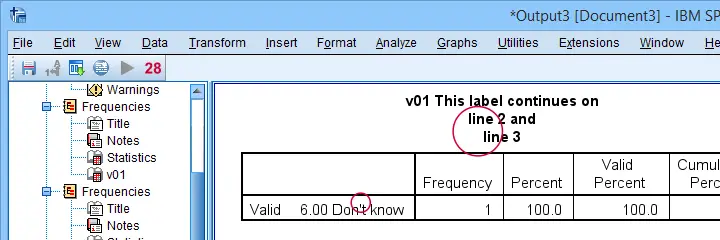
So those are basic escape sequences in SPSS syntax. Now, what about Python?
In Python, escaping is always done with a backslash. A backslash itself is also escaped by a backslash. Alternatively, specify a string as a raw string by preceding it with “r”. The syntax below shows some basic examples.
begin program python3.
vallab = 'Don\'t know'
print(vallab)
end program.
*ESCAPE BACKSLASH WITH BACKSLASH.
begin program python3.
rDir = 'D:\\analyses_example\\new-data'
print(rDir)
end program.
*ESCAPE BACKSLASH BY RAW STRING.
begin program python3.
rDir = r'D:\analyses_example\new-data'
print(rDir)
end program.
Comments in SPSS and Python
In SPSS we usually comment entire lines of syntax by
- starting some line with an asterisk and
- ending it with a period.
In rare cases, we may enter a comment within some command enclosed by /* and */ as shown below.
frequencies all /* AND HERE'S A COMMENT WITHIN A COMMAND */
/barchart.
In Python, everything between a hashtag and the end of the line in which it occurs is a comment. Alternatively, enclose a (multiline) comment by triple quotes.
begin program python3.
#FIRST GREET AUDIENCE BEFORE PROCEEDING
print('Hello!') #DONE
end program.
*PYTHON COMMENT BETWEEN TRIPLE SINGLE QUOTES.
begin program python3.
'''
This is a multiline
comment enclosed by
triple single quotes.
'''
print('Hello!')
end program.
Thanks for reading!
 SPSS TUTORIALS
SPSS TUTORIALS
THIS TUTORIAL HAS 5 COMMENTS:
By Linda Martell on July 15th, 2015
Really good!
By omkar on July 31st, 2016
In our company we are using SPSS v23 on windows 7.When i am trying to run the python code as you suggested in the previous section.I got the bellow error.
>Error # 6887. Command name: begin program
>External program failed during initialization.
>Execution of this command stops.
Please make sure that Essentials for Python has been successfully installed.
As per knowledge SPSS v23 dosen't require any additional download of it(defaulty installed). if so what are the ways to perfectly install Python Essentials in my PC.(before than how can i make sure that i have python essentials in my system( i didn't see any python essential installation file in my SPSS program files)).Secondly just to let you know i didn't install Python in my PC.Is it required to install it.
please help on this.
By Ruben Geert van den Berg on July 31st, 2016
Hi Omkar!
When you install a recent SPSS version, you'll be asked during the installation process whether you'd like to have the Python Essentials too. It seems you declined that so you have SPSS without the Python Essentials -like many other users by the way. I think the easiest fix is to uninstall and reinstall SPSS completely and make sure you do opt in for the Python Essentials.
Other users have reported that they added the Python Essentials to SPSS without reinstalling but I'm not entirely sure how they did it and how much effort it took them.
By Aravinda Thiagalingam on January 18th, 2019
Hi Ruben,
Thanks for tutorial! One other thing that is worth mentioning with python is that many objects - particularly lists are passed by reference and hence assigning a new variable to an old one and then changing the new variable will result in change the old one (as it is not a copy of the old list but just another pointer to it).
By Ruben Geert van den Berg on January 18th, 2019
Hi Aravinda, thanks for your comment!
Good point but I think it'll be over the heads of most of my audience.
Thanks!
SPSS tutorials