Summary
Reading multiple sheet Excel workbooks into SPSS is easily done with this Custom Dialog. This tutorial demonstrates how to use it.
Before You Start
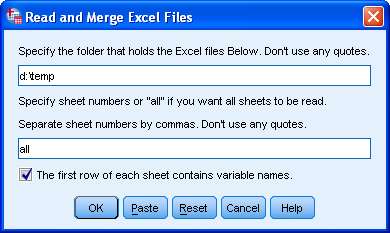 SPSS Read and Merge Excel Files Tool
SPSS Read and Merge Excel Files Tool
- Make sure you have the SPSS Python Essentials installed.
- Download and install the xlrd module.
- If you'd like to generate some test data as done in the syntax example, you'll need the xlwt module as well.
- Download and install Excel to SPSS Tool. Note that this is an SPSS custom dialog. You'll now find under .
- Close all datasets in SPSS.
SPSS Syntax Example for Generating Test Data
* Create some small Excel workbooks for testing.
begin program.
rdir=r'd:\temp' # Specify folder for writing test files.
import xlwt,random,datetime,os
fmt = xlwt.easyxf(num_format_str='M/D/YY')
wBooks = ["book_" + str(cnt) for cnt in range(1,5)]
for noSheets,wBook in enumerate(wBooks):
wb=xlwt.Workbook()
for sheetNo in range(noSheets + 1):
ws=wb.add_sheet("sheet_%d"%(sheetNo + 1))
for col,cont in enumerate(['date','ID','JobTitle','Revenue']):
ws.write(0,col,cont)
for row in range(1,6):
ws.write(row,0,datetime.datetime(2008 + sheetNo,1,1) + datetime.timedelta(days=random.randrange(1,365)),fmt)
ws.write(row,1,random.choice([None,104,21,60,2,1030]))
ws.write(row,2,random.choice([None,'Developer','Tester','Manager']))
ws.write(row,3,random.randrange(40,80)*1000)
wb.save(os.path.join(rdir,wBook + '.xls'))
end program.
begin program.
rdir=r'd:\temp' # Specify folder for writing test files.
import xlwt,random,datetime,os
fmt = xlwt.easyxf(num_format_str='M/D/YY')
wBooks = ["book_" + str(cnt) for cnt in range(1,5)]
for noSheets,wBook in enumerate(wBooks):
wb=xlwt.Workbook()
for sheetNo in range(noSheets + 1):
ws=wb.add_sheet("sheet_%d"%(sheetNo + 1))
for col,cont in enumerate(['date','ID','JobTitle','Revenue']):
ws.write(0,col,cont)
for row in range(1,6):
ws.write(row,0,datetime.datetime(2008 + sheetNo,1,1) + datetime.timedelta(days=random.randrange(1,365)),fmt)
ws.write(row,1,random.choice([None,104,21,60,2,1030]))
ws.write(row,2,random.choice([None,'Developer','Tester','Manager']))
ws.write(row,3,random.randrange(40,80)*1000)
wb.save(os.path.join(rdir,wBook + '.xls'))
end program.
Reading All Data Into SPSS
Since we created our test data in
d:\temp, this folder will hold the Excel files. We can simply copy-paste this into the dialog. Other than that, we don't have to change anything. The first row holds the variable names and we'd like all sheets from all workbooks to be read.Description
- By default, the program will read in all .xls files in a folder specified by the user.
- By default, all data from all sheets will be imported. The default of all sheets can be overridden by specifying one or more sheets (see below).
- In order for this to make sense, all sheets in all workbooks are assumed to have similar formats (numbers of columns, column contents).
- By default, it is assumed that the first row of each sheet contains column names. If these conflict, the column names of the last sheet of the last workbook that's read will be used. If no column names are present,
column_1,column_2and so on will be used as variable names in SPSS.
Converting Date Variables
Date variables in the Excel files are not automatically converted to SPSS date variables. After reading in the data, they can be converted with the syntax below.
* Convert "date" to date format.
compute date=datesum(date.dmy(30,12,1899),date,"days").
format date(edate10).
exe.
compute date=datesum(date.dmy(30,12,1899),date,"days").
format date(edate10).
exe.
What if I Don't Want All Sheets to be Read?
- In this case, the desired sheets can be specified. Note that the first sheet is referenced by 1 (rather than 0).
- If two or more sheets are to be read, separate them with commas.
- If sheets that are specified do not exist in one or more workbooks, the command will not run. An error message will indicate the first workbook where this occurred.
What if I Don't Want All Workbooks to be Read?
This default can not be overridden. A workaround may be to move irrelevant workbooks to a different folder.
 SPSS TUTORIALS
SPSS TUTORIALS
THIS TUTORIAL HAS 17 COMMENTS:
By Ruben Geert van den Berg on May 2nd, 2017
Hi Tal!
The error is telling you that you did not properly install the xlrd module module. I should add that this has been giving people headaches for ages.
Second, my syntax uses Python 2.7 so you shouldn't try to run it in Python3 as these are not backwards compatible.
Hope that helps!
By Tal Spalter on May 2nd, 2017
Hello Ruben,
I installed xlrd several times but it doesn't matter. Still am getting the same error. Should I uninstall python 3 and reinstall python 2.7 so it might work?
Thanks,
Tal.
By Ruben Geert van den Berg on May 3rd, 2017
Hi Tal!
Which SPSS version are you using? Modern versions have Python2.x and Python3.x installed if you tick "Python Essentials..." during the installation process. Having both Python versions should not be a problem if you select the right xlrd version (for Python2.x, that is). Please note that modern SPSS versions have Python installed in the SPSS installation folder rather than
c:\python27and this is relevant to properly installing xlrd.But -again- lots of people are having troubles getting xlrd working with SPSS. The post I wrote on it works for most -but not all- SPSS users.
Keep up the good mood, though! Rome wasn't built in a day either...
By Kim on June 14th, 2018
Dear Ruben,
I've been blowing my head trying to make your Read And Merge Excel Files work.
I just installed SPSS 24 WITH Python Essentials.
I did not have any previous python version installed.
I did the "environment variables" thing, making it point to C:\Program Files\IBM\SPSS\Statistics\24\Python (python 2.7.6's dir).
I can't get passed through your test with xlwt (which i successfully installed following your indications).
SPSS says (spanish, sorry):
>Número de error 5712 en columna 8. Texto: xlwt
>Se espera un nombre de subcomando IMPORT válido, pero no se ha encontrado.
>Los subcomandos reconocidos son FILE, TYPE, KEEP, DROP, RENAME y MAP.
>La ejecución de este comando se detiene.
Any help would be highly appreciated.
Thanks.
Kim.
By Ruben Geert van den Berg on June 14th, 2018
Hi Kim!
You get this error when you write
import ...instead of
begin program.import ...
end program.